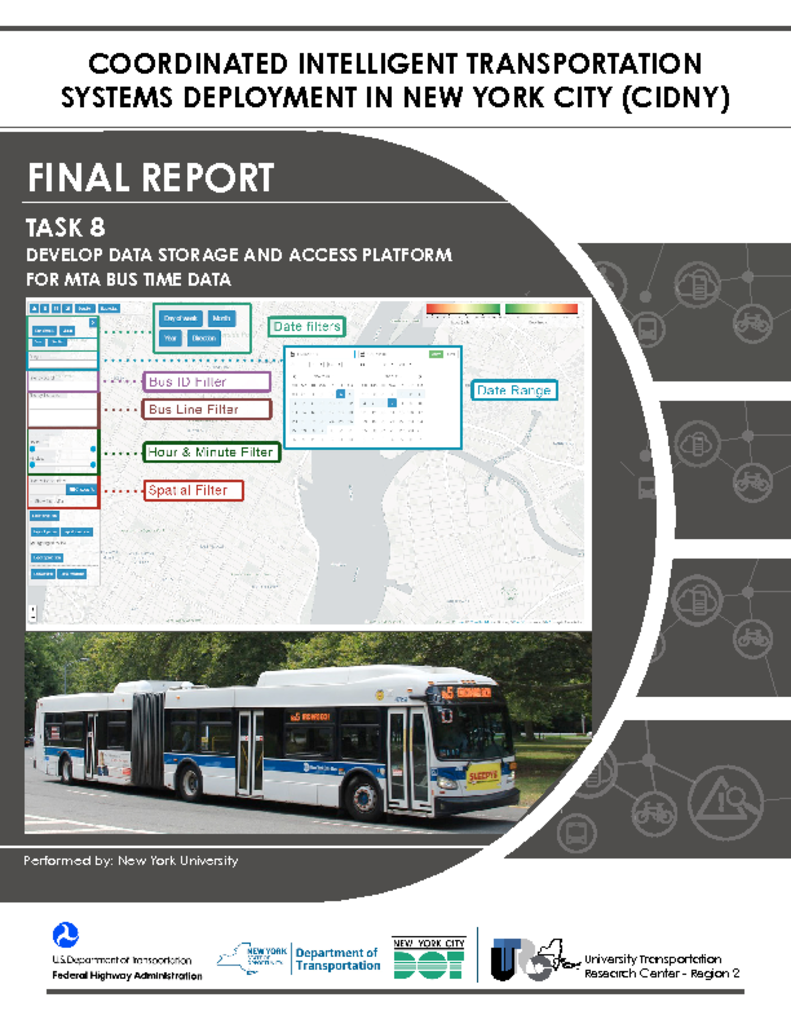
Travel times can be collected from a large number of potential sources. Conventionally, fixed detectors such as inductive loops embedded in the roadway have been used to measure vehicle flows and estimate speeds. Recent technological advances and the widespread deployment of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) in consumer devices make mobile data sources a promising and potentially cost-effective way to monitor the congestion in a transportation system. New York City Department of Transportation (NYCDOT) along with many other DOTs in the region and around the country have been using probe vehicle data for monitoring time-dependent traffic conditions and conducting before and after studies of various transportation projects. Specifically, NYCDOT has been using probe vehicle data from yellow taxis and other vehicles equipped with GPS as well as the TRANSMIT system. In this project, NYCDOT wants to automate and enhance their use of Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) bus data that they are already acquiring under a protocol developed between the two agencies. The overall goal of improving the current MTA bus data acquisition, processing, storage and querying procedures for NYCDOT comprised of 3 main tasks: The first task is to develop efficient data acquisition, storage, maintenance, querying, and visualization procedures to automate and improve the overall process of using MTA bus data. The second task is to create a web-based application that takes advantage of the MTA’s on-going in- house data development efforts as well New York University (NYU) Center for Urban Science and Progress’ (CUSP) extensive resources and expertise in the area of big data management. The third task is to provide recommendations to enhance the developed tool based on the experience obtained throughout this project and to incorporate this developed app and its functionalities into NYCDOT operations in a more routine manner.